DROPSHIPPING (local)

Title: The Ins and Outs of Drop Shipping: A Financial Perspective
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, entrepreneurs are constantly seeking innovative ways to establish and grow their ventures. One such method that has gained substantial traction is drop shipping. This unique business model not only offers opportunities for budding entrepreneurs to start their own businesses with minimal upfront costs but also presents distinct financial considerations that can significantly impact the bottom line. In this blog, we'll dive into the world of drop shipping from a financial standpoint, exploring its benefits, challenges, and key strategies for success.
Understanding Drop Shipping: A Brief Overview
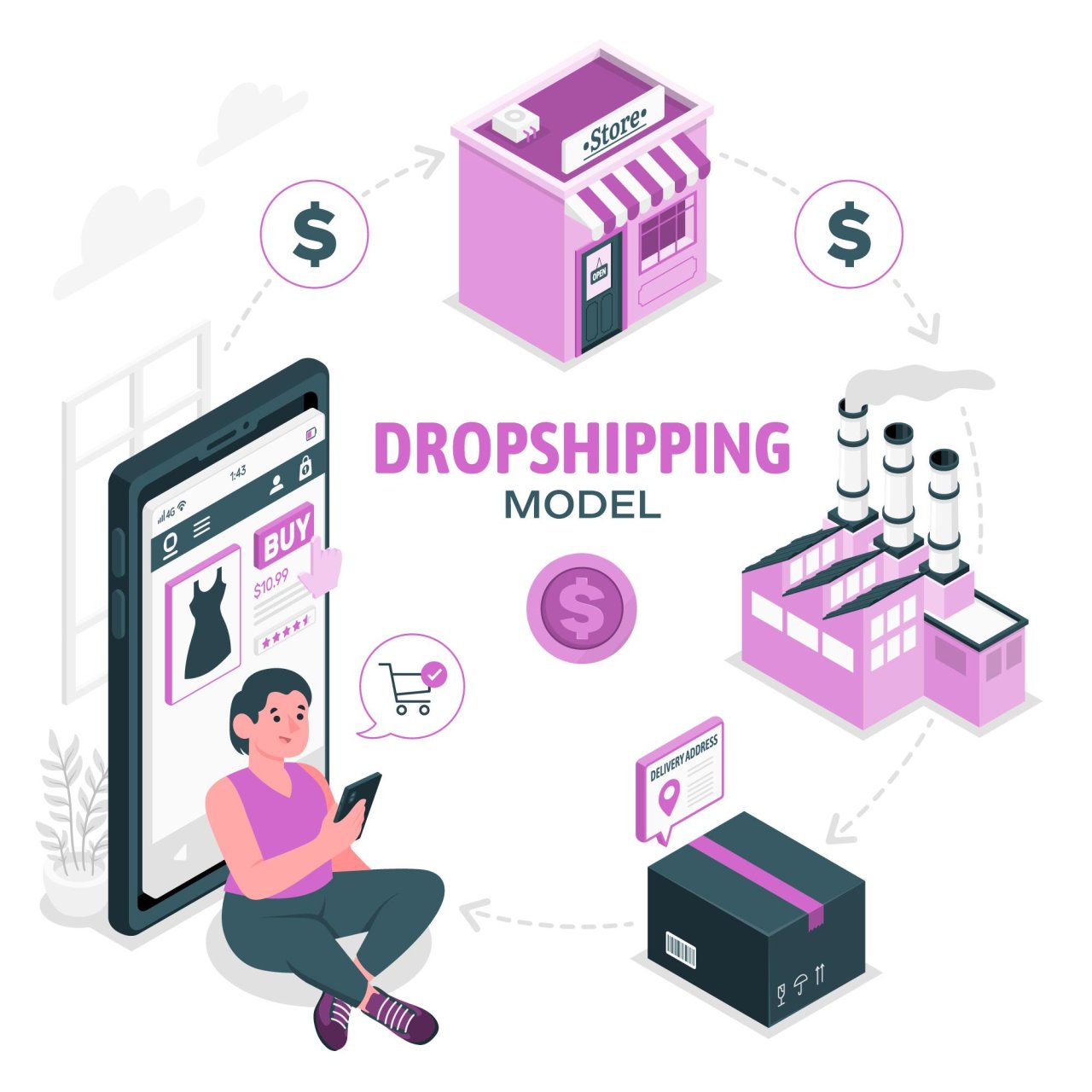
Drop shipping is an e-commerce fulfillment method where retailers do not hold physical inventory. Instead, they partner with suppliers who house and manage inventory. When a customer places an order, the retailer forwards the order details to the supplier, who then ships the product directly to the customer. The retailer's role primarily involves marketing, sales, and customer service.
Financial Benefits of Drop Shipping:
1. Low Initial Investment: Unlike traditional retail models, drop shipping doesn't require a significant upfront investment in inventory. Entrepreneurs can start their online stores with minimal capital, reducing financial risk.
2. Reduced Overhead Costs: Drop shippers avoid costs related to warehousing, storage, and inventory management. This allows businesses to allocate resources to other critical areas, such as marketing and customer acquisition.
3. Wider Product Range: Without the constraints of physical inventory, drop shippers can offer a diverse range of products to their customers. This flexibility can attract a broader audience and cater to niche markets.
Challenges and Financial Considerations:
1. Thin Profit Margins: While drop shipping eliminates the need for inventory management costs, the competitive nature of the market can lead to lower profit margins due to price competition and supplier fees.
2. Quality Control: Entrepreneurs must rely on suppliers for product quality and timely shipping. Inconsistent quality or delayed shipments can lead to customer dissatisfaction, returns, and potential financial losses.
3. Customer Service Costs: Since the retailer is responsible for customer service, addressing inquiries, concerns, and returns can incur additional costs and time commitments.
Strategies for Financial Success in Drop Shipping:
1. Thorough Supplier Research: Carefully vet potential suppliers to ensure their reliability, product quality, and shipping times. Establish clear communication channels to resolve issues promptly.
2. Pricing Strategy: Factor in all costs, including product price, shipping fees, marketing expenses, and overhead, when determining your product prices. Striking the right balance between competitiveness and profitability is crucial.
3. Focus on Marketing: Invest in effective marketing strategies to drive traffic to your online store. A well-executed marketing campaign can lead to increased sales, compensating for thin profit margins.
4. Automation Tools: Utilize e-commerce platforms and software that offer automation for order processing, inventory tracking, and customer communication. Automation can streamline operations and reduce human errors.
Conclusion:
Drop shipping presents an enticing opportunity for entrepreneurs to enter the world of e-commerce without the burden of inventory management. While the financial benefits are evident, a clear understanding of the challenges and careful planning are essential for long-term success. By selecting reliable suppliers, implementing effective pricing strategies, and focusing on exceptional customer service, drop shippers can navigate the financial landscape and build profitable and sustainable businesses in the dynamic e-commerce realm.
 English
English French
French












